This facility is designed to remove pollutants
and odors generated from facilities that release air pollutants.
Facility introduction

VOCs and odors at industrial sites are removed through combustion (oxidation) at temperatures ranging from 750 to 850 °C. The heat generated during the process is absorbed and reused for heat storage, making it an energy-efficient air pollution contro facility. It can be applied to various industrial sites, including semiconductor, display, film coating, painting, tire, plastic, synthetic resin, steel, automobiles, and chemicals.
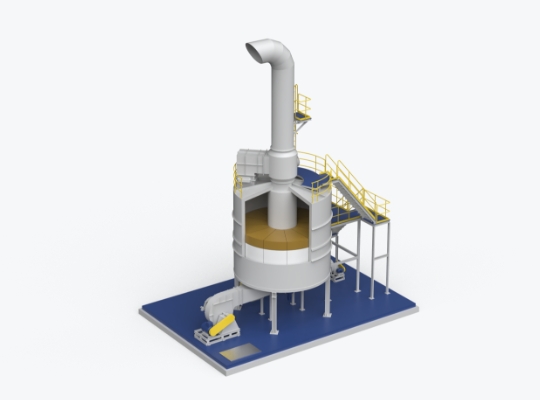

This air pollution control facility’s basic structure and principles are similar to that of RTO, but catalysts are utilized to lower the combustion temperature to 300–500 °C, thereby enhancing energy efficiency. Another advantage is the lower production of thermal NOx due to the lower operating temperature. However, process is not applicable to sites where components that catalytic poisoning are emitted.

- The air pollution control facility uses catalysts to combust and remove VOCs and odors at around 300 °C.
- The air-tight system minimizes gas leakage, and ensures high efficiency in removing harmful gases.
- The low operating temperature suppresses the generation of thermal NOx.
- The facility uses a manganese-based catalyst to oxidize and remove VOCs.
- The operating temperature is around 200℃, exhibiting excellent low-temperature activity compared to other facilities.
- It boasts outstanding performance in odor removal.

